Firewalld防火墙详解
众所周知,在RHEL7系统中,firewalld防火墙取代了iptables防火墙。我们都知道iptables的防火墙策略是交由内核层面的netfilter网络过滤器来处理的,而firewalld则是交由内核层面的nftables包过滤框架来处理。 相较于iptables防火墙而言,firewalld支持动态更新技术并加入了区域(zone)的概念。简单来说,区域就是firewalld预先准备了几套防火墙策略集合(策略模板),用户可以根据生产场景的不同而选择合适的策略集合,从而实现防火墙策略之间的快速切换。
Firewalld provides a dynamically managed firewall with support for network/firewall zones to define the trust level of network connections or interfaces. It has support for IPv4, IPv6 firewall settings and for ethernet bridges and has a separation of runtime and permanent configuration options. It also supports an interface for services or applications to add firewall rules directly.
基本概念
区域
表1:firewalld中常用的区域名称及策略规则
| 区域(zone) | 默认策略规则 |
|---|---|
| trusted | 允许所有的数据包进出 |
| home | 拒绝进入的流量,除非与出去的流量相关;而如果流量与ssh、mdns、ipp-client、amba-client与dhcpv6-client服务相关,则允许进入 |
| Internal | 等同于home区域 |
| work | 拒绝进入的流量,除非与出去的流量相关;而如果流量与ssh、ipp-client与dhcpv6-client服务相关,则允许进入 |
| public | 拒绝进入的流量,除非与出去的流量相关;而如果流量与ssh、dhcpv6-client服务相关,则允许进入 |
| external | 拒绝进入的流量,除非与出去的流量相关;而如果流量与ssh服务相关,则允许进入 |
| dmz | 拒绝进入的流量,除非与出去的流量相关;而如果流量与ssh服务相关,则允许进入 |
| block | 拒绝进入的流量,除非与出去的流量相关 |
| drop | 拒绝进入的流量,除非与出去的流量相关 |
These are the zones provided by firewalld sorted according to the default trust level of the zones from untrusted to trusted:
drop : Any incoming network packets are dropped, there is no reply. Only outgoing network connections are possible.
block : Any incoming network connections are rejected with an icmp-host-prohibited message for IPv4 and icmp6-adm-prohibited for IPv6. Only network connections initiated within this system are possible.
public : For use in public areas. You do not trust the other computers on networks to not harm your computer. Only selected incoming connections are accepted.
external : For use on external networks with masquerading enabled especially for routers. You do not trust the other computers on networks to not harm your computer. Only selected incoming connections are accepted.
dmz : For computers in your demilitarized zone that are publicly-accessible with limited access to your internal network. Only selected incoming connections are accepted.
work : For use in work areas. You mostly trust the other computers on networks to not harm your computer. Only selected incoming connections are accepted.
home : For use in home areas. You mostly trust the other computers on networks to not harm your computer. Only selected incoming connections are accepted.
internal : For use on internal networks. You mostly trust the other computers on the networks to not harm your computer. Only selected incoming connections are accepted.
trusted : All network connections are accepted.
动静态更新技术之间的区别:iptables每一个更改都需要先清除所有旧有的规则,然后重新加载所有的规则(包括新的和修改后的规则);而firewalld任何规则的变更都不需要对整个防火墙规则重新加载。
配置
firewalld服务的主配置文件是firewalld.conf,防火墙策略的配置文件是以xml格式为主,存放在以下两个目录里。
1 | /etc/firewalld # 用户配置文件 |
firewalld有基于CLI(命令行界面)和基于GUI(图形用户界面)两种管理方式,即:firewall-cmd(终端管理工具)和firewall-config(图形管理工具)。
firewalld的参数一般都是以“长格式”来提供的,但是在RHEL7系统里支持部分命令的参数补齐,其中就包括firewall-cmd命令,也就是说可以用Tab键来补齐长格式参数,很酷吧。
命令
表2:firewall-cmd命令中使用的参数以及作用
| 参数 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| --get-default-zone | 查访默认的区域名称 |
| --set-default-zone=<区域名称> | 设置默认的区域,使其永久生效 |
| --get-zones | 显示可用的区域 |
| --get-services | 显示预定义的服务 |
| --get-active-zones | 显示当前正在使用的区域、来源地址和网卡名称 |
| --add-source= | 将源自此IP或子网的流量导向指定的区域 |
| --remove-source= | 不再将源自此IP或子网的流量导向这个区域 |
| --add-interface=<网卡名称> | 将源自该网卡的所有流量都导向某个指定区域 |
| --change-interface=<网卡名称> | 将某个网卡与区域进行关联 |
| --list-all | 显示当前区域的网卡配置参数、资源、端口以及服务等信息 |
| --list-all-zones | 显示所有区域的网卡配置参数、资源、端口以及服务等信息 |
| --add-service=<服务名> | 设置默认区域允许该服务的流量 |
| --add-port=<端口号/协议> | 设置默认区域允许该端口的流量 |
| --remove-service=<服务名> | 设置默认区域不再允许该服务的流量 |
| --remove-port=<端口号/协议> | 设置默认区域不再允许该端口的流量 |
| --reload | 让“永久生效”的配置规则立即生效,并覆盖当前的配置规则 |
| --panic-on | 开启应急状况模式 |
| --panic-off | 关闭应急状况模式 |
firewalld配置的防火墙策略默认为运行时(Runtime)模式,又称为当前生效模式,而且随着系统的重启会失效。如果想让配置策略一直存在,就需要使用永久(Permanent)模式了,方法就是在firewall-cmd命令后面添加--permanent参数,这样配置的防火墙策略就可以永久生效了。但是,永久生效模式有一个“不近人情”的特点,就是使用它设置的策略只有在系统重启后才会生效。如果想让配置的永久策略立即生效,需要手动执行firewall-cmd --reload命令。
注:remove掉ssh服务或者ssh端口,当前远程登陆会话不会断开,退出后就无法远程连接了。
firewalld服务启动、重启、停止
1 | systemctl start firewalld |
重新加载防火墙配置 firewall-cmd --reload
查看firewalld的运行状态 firewall-cmd --state
查看默认当前使用的区域
firewall-cmd --get-default-zone
查看系统默认活动区域名称、来源地址和关联的网卡
firewall-cmd --get-active-zones
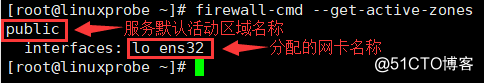
查看所有可用区域 firewall-cmd --get-zones
查看区域的所有设置
1 | firewall-cmd --zone=internal --list-all |
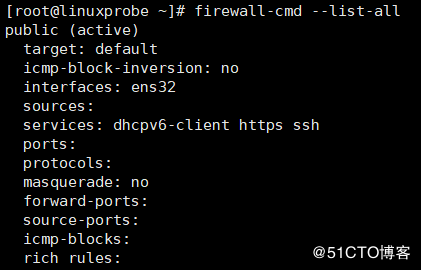
Target:目标 icmp-block-inversion:ICMP协议类型黑白名单开关(yes/no) Interfaces:关联的网卡接口 sources:来源,可以是IP地址,也可以是mac地址 services:允许的服务 ports:允许的目标端口,即本地开放的端口 protocols:允许通过的协议 masquerade:是否允许伪装(yes/no),可改写来源IP地址及mac地址 forward-ports:允许转发的端口 source-ports:允许的来源端口 icmp-blocks:可添加ICMP类型,当icmp-block-inversion为no时,这些ICMP类型被拒绝;当icmp-block-inversion为yes时,这些ICMP类型被允许。 rich rules:富规则,即更细致、更详细的防火墙规则策略,它的优先级在所有的防火墙策略中也是最高的。
开始
查看所有预设的服务 firewall-cmd --get-services
此时将会列出/usr/lib/firewalld/services/目录中所有的服务名称。
查看所有区域的设置 firewall-cmd --list-all-zones
查看指定网卡所在的区域
firewall-cmd --get-zone-of-interface=ens32
把firewalld的当前默认区域设置为drop,此为永久设置
firewall-cmd --set-default-zone=drop
把ens32网卡关联的区域修改为drop
1 | firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=drop --change-interface=ens32 # 永久设置 |
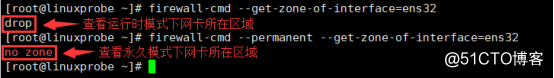
我们后面的设置命令将全部使用运行时模式,即当前生效模式。 将来自ens33网卡的流量都作用到默认的drop区域
1 | firewall-cmd --zone=drop -add-interface=ens33 # 作用在指定区域 |
注:不指定--zone参数的话,将会对默认区域进行设置 启动关闭firewalld防火墙服务的应急状况模式,远程连接服务器时请慎用
1 | firewall-cmd --panic-on |
设置一个来源地址作用在drop区域上面
1 | firewall-cmd --zone=drop --add-source=192.168.1.12 # 作用在指定区域 |
说明:凡是IP为192.168.1.12发来包将会使用drop区域设置的规则
对于一个接收到的请求具体使用哪个zone,firewalld是通过三种方式来判断的:
1、source,来源地址 2、Interface,接收请求的网卡 3、firewalld配置的默认区域(zone)
这三个方式的优先级按顺序依次降低,也就是说如果按照source可以找到就不会再按interface去找,如果前两个都找不到才会使用第三个默认区域。 查询drop区域是否允许请求ssh和https服务的流量
常用命令
在drop区域开放https服务
firewall-cmd --zone=drop --add-service=https
取消开放https服务,即禁止https服务
firewall-cmd --zone=drop --remove-service=https
开放22端口
firewall-cmd --zone=drop --add-port=22/tcp
取消开放22端口
firewall-cmd --zone=drop --remove-port=22/tcp
开放8080和8081端口
firewall-cmd --zone=drop --add-port=8080-8081/tcp
查询drop区域开放了哪些端口
firewall-cmd --zone=drop --list-ports
允许icmp协议流量,即允许ping
firewall-cmd --zone=drop --add-protocol=icmp
取消允许icmp协议的流量,即禁ping
firewall-cmd --zone=drop --remove-protocol=icmp
查询drop区域开放了哪些协议
firewall-cmd --zone=drop --list-protocols
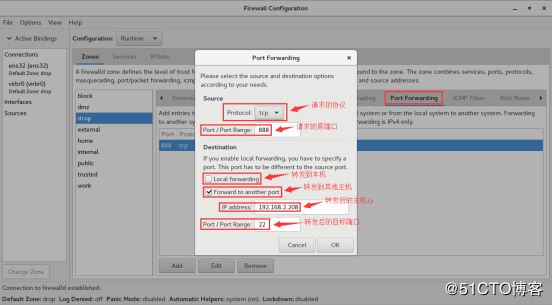
端口转发
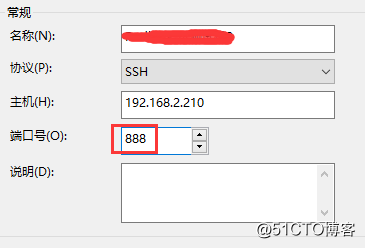
将原本访问本机888端口的流量转发到本机22端口
firewall-cmd --zone=drop --add-forward-port=port=888:proto=tcp:toport=22
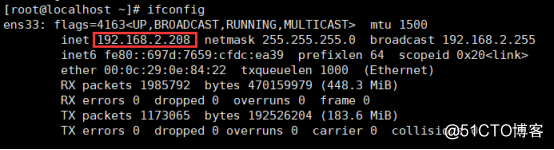
将原本访问本机888端口的流量转发到ip为192.168.2.208的主机的22端口,需要开启masquerade
1 | firewall-cmd --zone=drop --add-masquerade |
测试端口转发功能是否生效 在客户端尝试访问192.168.2.210主机的888端口,连上去后发现实际连接的是192.168.2.208主机,测试OK。
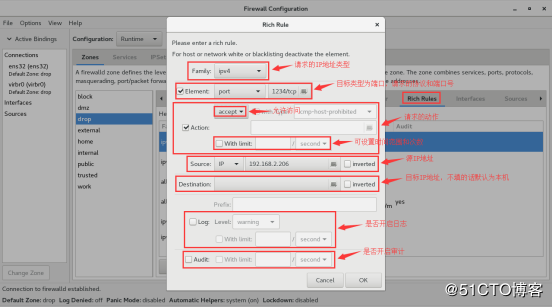
富规则
接下来我们来看富规则的设置,即 rich rules
允许192.168.2.208主机的所有流量
firewall-cmd --zone=drop --add-rich-rule="rule family="ipv4" source address="192.168.2.208" accept"
允许192.168.2.208主机的icmp协议,即允许192.168.2.208主机ping
firewall-cmd --add-rich-rule="rule family="ipv4" source address="192.168.2.208" protocol value="icmp" accept"
取消允许192.168.2.208主机的所有流量
firewall-cmd --zone=drop --remove-rich-rule="rule family="ipv4" source address="192.168.2.208" accept"
允许192.168.2.208主机访问ssh服务
firewall-cmd --zone=drop --add-rich-rule="rule family="ipv4" source address="192.168.2.208" service name="ssh" accept"
禁止192.168.2.208访问https服务,并返回错误信息
firewall-cmd --zone=drop --add-rich-rule="rule family="ipv4" source address="192.168.2.208" service name="https" reject"
注:如果是drop的话是直接丢弃,会返回timeout(连接超时)
允许192.168.2.0/24网段的主机访问22端口
firewall-cmd --zone=drop --add-rich-rule="rule family="ipv4" source address="192.168.2.0/24" port protocol="tcp" port="22" accept"
每分钟允许2个新连接访问ftp服务
firewall-cmd --add-rich-rule="rule service name=ftp limit value=2/m accept"
允许新的ipv4和ipv6连接ftp,并使用日志和审核,每分钟允许访问一次
firewall-cmd --add-rich-rule="rule service name=ftp log limit value="1/m" audit accept"
拒绝来自192.168.2.0/24网段的连接,10秒后自动取消
firewall-cmd --add-rich-rule="rule family=ipv4 source address=192.168.2.0/24 reject" --timeout=10
允许ipv6地址为2001:db8::/64子网的主机访问dns服务,并且每小时审核一次,300秒后自动取消
firewall-cmd --add-rich-rule="rule family=ipv6 source address="2001:db8::/64" service name="dns" audit limit value="1/h" reject" --timeout=300
将来自192.168.2.0/24网段访问本机80端口的流量转发到本机的22端口
firewall-cmd --zone=drop --add-rich-rule="rule family=ipv4 source address=192.168.2.0/24 forward-port port=80 protocol=tcp to-port=22"
将来自192.168.2.0/24网段访问本地80端口的流量转发到192.168.2.208主机的22端口
firewall-cmd --zone=drop --add-rich-rule="rule family=ipv4 source address=192.168.2.0/24 forward-port port=80 protocol=tcp to-port=22 to-addr=192.168.2.208"
伪装,将来自局域网192.168.2.0/24网段访问外网的流量映射为网络出口公网IP,即修改源IP地址
1 | firewall-cmd --zone=drop --add-masquerade |
好了,写的差不多了,工作中基本上够用了
GUI配置
在RHEL7之前的发行版本默认的防火墙中,几乎没有图形化的防火墙管理工具,但是firewalld却有,firewall-config是firewalld防火墙配置管理工具的GUI(图开用户界面)版本,几乎可以实现所有命令行执行的操作。即使没有扎实的Linux命令基础,也完合可以通过它来妥善配置firewalld防火墙策略。Firewall-config的界面如下图所示,功能具体如下:
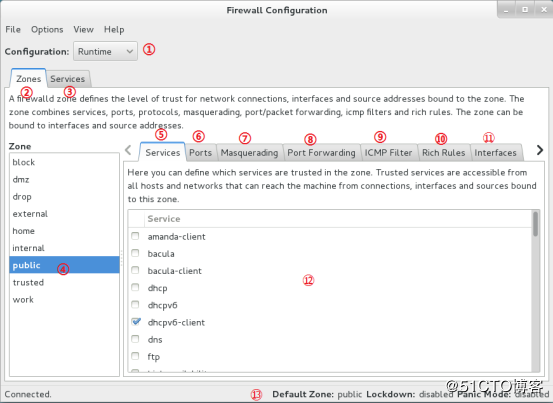
1、选择运行时(Runtime)模式或永久(Permanent)模式。 2、可选的策略集合区域列表。 3、常用的系统服务列表。 4、当前正在使用的区域。 5、管理当前被选中区域中的服务。 6、管理当前被选中区域中的端口。 7、开启或关闭SNAT(源地址转换协议)技术。 8、设置端口转发策略。 9、控制请求icmp服务的流量。 10、管理防火墙的富规则。 11、管理网卡设备。 12、被选中区域的服务,若勾选了相应服务前面的复选框,则表示允许与之相关的流量。 13、Firewall-config工具的运行状态。
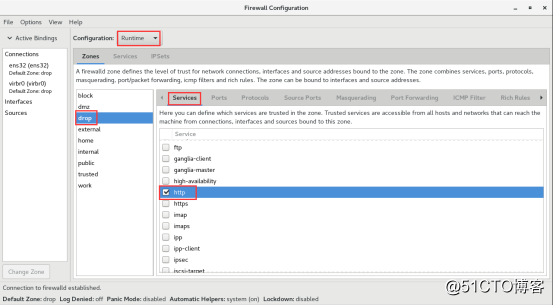
对外开放http服务,如下图
添加一条防火墙规则,使其放行访问8080-8088端口(TCP协议)的流量,并且永久生效
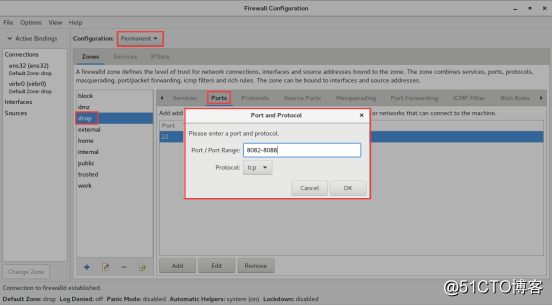
单击Options菜单中的Reload Firewalld选项,让上面配置的永久规则立即生效,这与在命令行中执行--reload参数的效果一样。
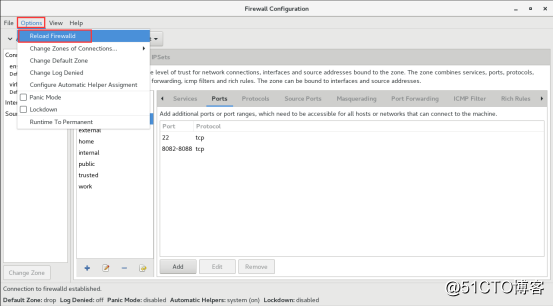
SNAT技术相信很多人都知道,那现在我们来开启SNAT技术,其实就是命令行下的masquerade。
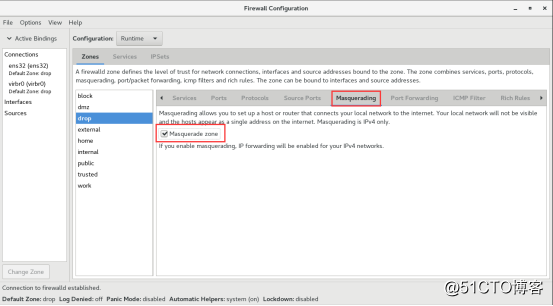
下面我们来配置一个端口转发规则,将888端口的流量转发到其他主机的22端口上。 注:转发本机端口不需要开启masquerade,转发到别的主机才需要开启masquerade。
配置富规则,允许192.168.2.206主机访问本机的1234端口号
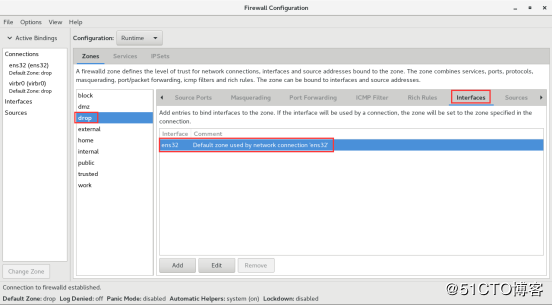
最后来看一下区域和网卡的关联,增加网卡的话只需要输入网卡名称即可。
下面是我自己写的一个简单的防火墙初始化脚本,5210是ssh端口号,192.168.2.208是保垒机,192.168.2.206是备用ssh机器。
1 | systemctl stop firewalld |
Enable and Disable firewalld
firewalld provides an init script for systems using classic SysVinit and also a systemd service file. The following documentation is about the systemd service used in Fedora, RHEL and CentOS distributions.
It is not recommended to use iptables directly while firewalld is running as this could lead into some unexpected issues. If a user, for example, is removing base rules or chains of the chain structure, then a firewalld reload might be needed to create them again.
Install and enable firewalld
If the iptables, ip6tables, ebtables and ipset services are in use:
1 | systemctl disable --now iptables.service |
To check the firewall state you have different options. The fist
option is to use systemctl status firewalld the other one
is to use firewall-cmd --state.
The output of the systemctl command should look like this:
1 | $ systemctl status firewalld |
The output of the firewall-cmd command should look like this:
1 | $ firewall-cmd --state |
Install and enable iptables, ip6tables, ebtables and ipset services
If firewalld is enabled and you want to enable the iptables, ip6tables, ebtables and ipset services instead:
1 | dnf install iptables-services ebtables ipset-service |
The use of the mask line is recommended as systemd will start firewalld if there is another service requires it or if the D-Bus interface of firewalld is used. If the service only gets disabled, then it will not be auto started anymore.